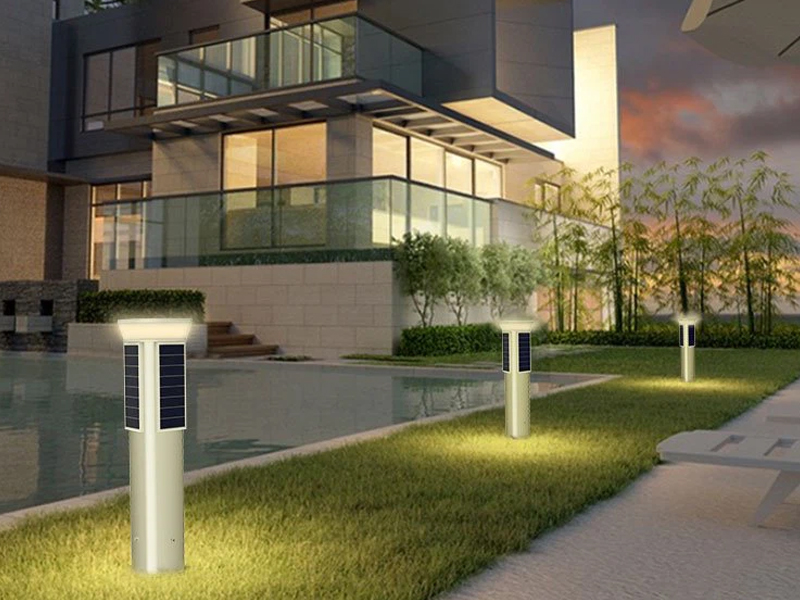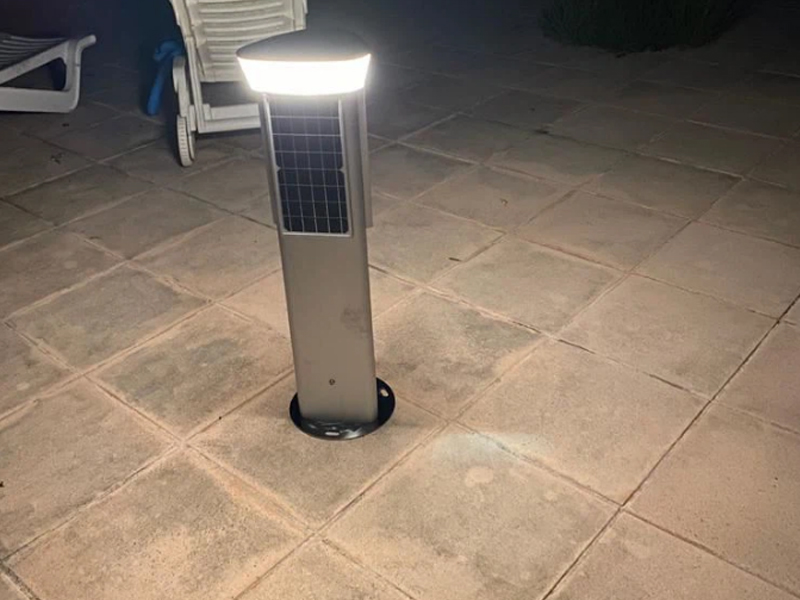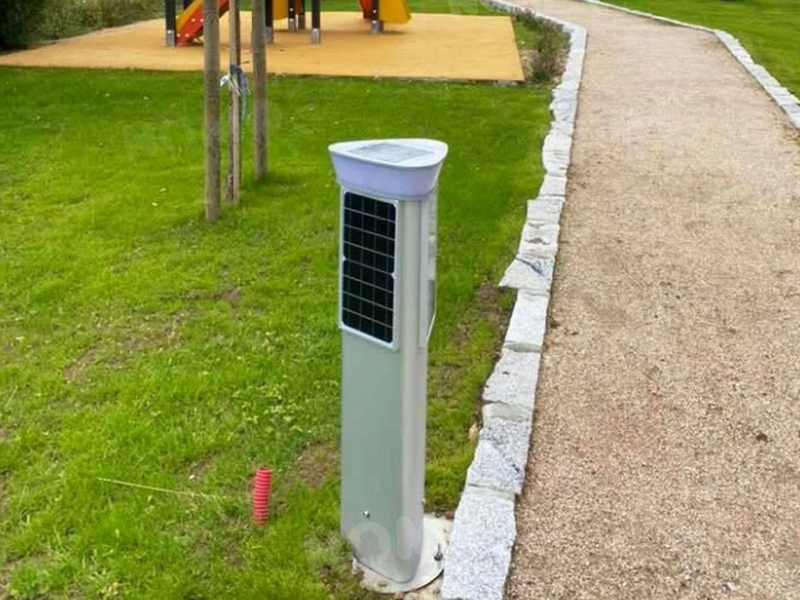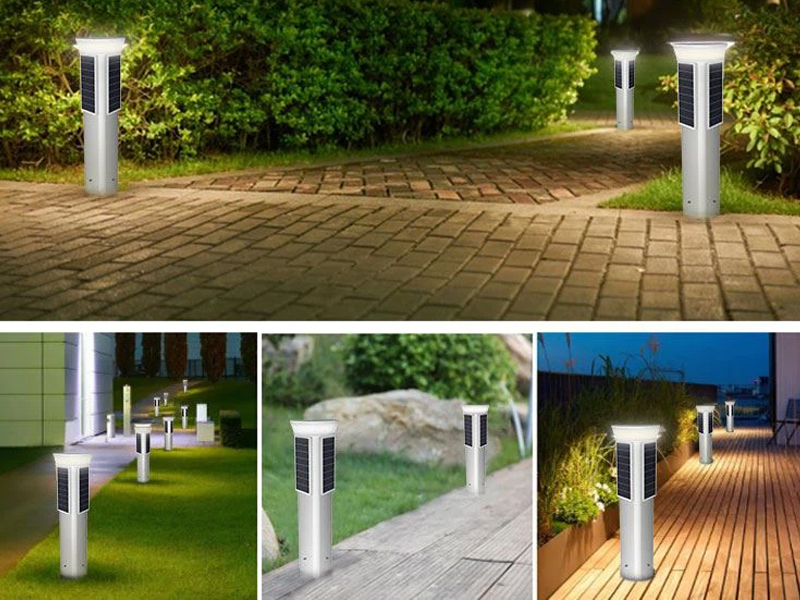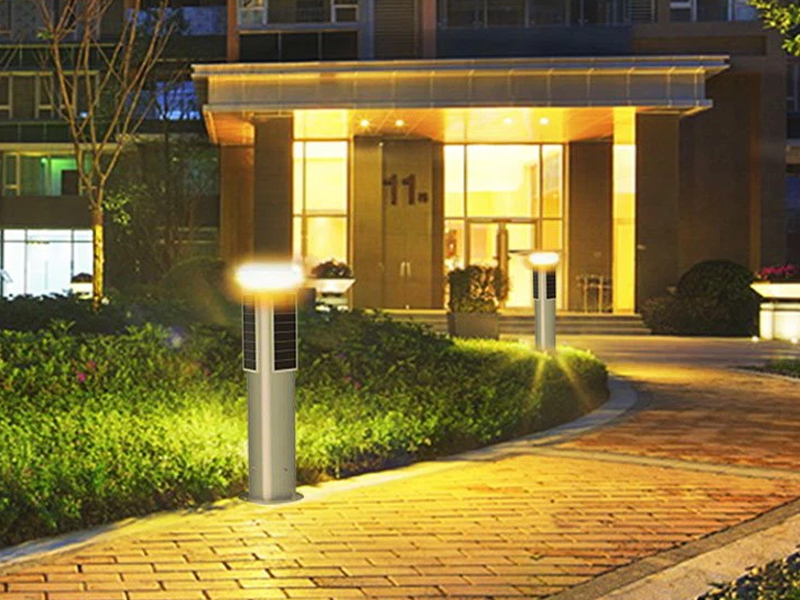
The Rise Of Thin-film Solar Cells
Speaking of solar cells, silicon crystals are currently the dominant industry in this industry, and silicon crystals are made of refined silicon. This module has existed as the basic technology of solar energy for more than 50 years. Since the first silicon solar cell was invented in 1954, its number has increased rapidly. At present, 12% to 18% of solar radiation converted into electrical energy is realized through it.
Crystalline silicon materials still dominate the materials for solar photovoltaic cells, but there have been many breakthroughs in thin-film photovoltaic cell technology in recent years. In 2005, crystalline silicon accounted for more than 95% of the solar photovoltaic cell market. However, since that time, the market share of thin-film photovoltaic materials has steadily increased year by year, and today it has accounted for 25% of the market. Hundreds of companies engaged in thin film photovoltaic technology have entered a new stage of R&D and production.
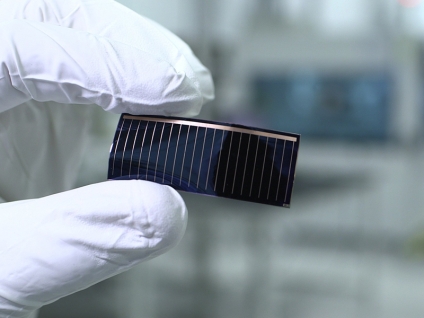
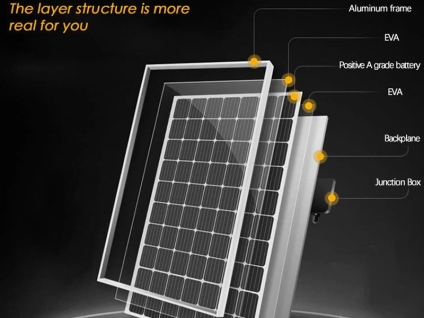
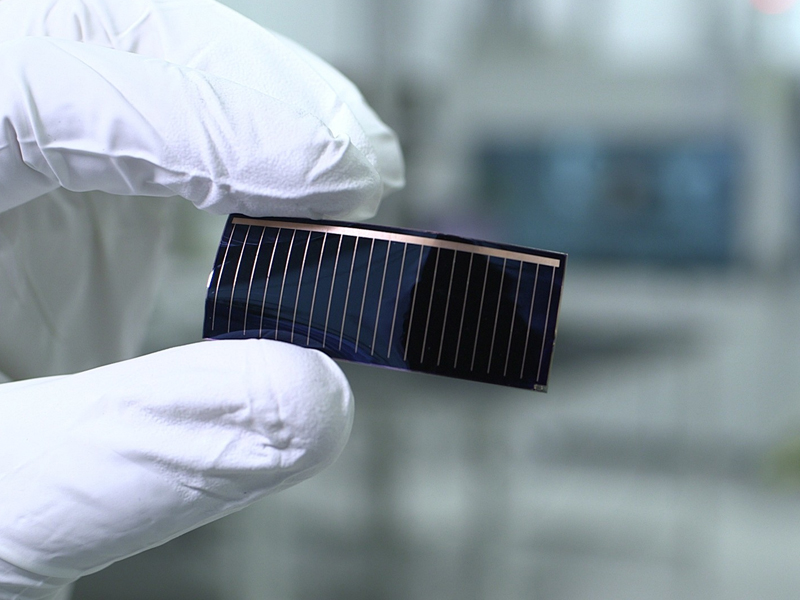
Large-area and laminated thin-film photovoltaic products have been commercialized since the 1990s. At present, the energy conversion efficiency of thin-film photovoltaic products has reached 6% to 11%. The higher the energy conversion efficiency, the less area and other auxiliary equipment required to generate a certain amount of electricity, which is a very cost-effective thing. At present, the conversion efficiency of thin-film solar cells is still far from that of crystalline silicon, but compared with crystalline silicon, thin-film solar cells have huge advantages in other aspects. The most important point is the low production cost of thin-film solar cells. Many thin-film solar panels are made of amorphous silicon, and high-grade silicon is used when preparing silicon crystalline solar panels. In addition, thin-film solar cells can also be made of other semiconductor materials, including copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) materials and cadmium telluride materials.